SAP Sales and Distribution (SD) is one of the most popularly used modules that is imparted in SAP SD Certification program towards better data and work management in enterprises. SAP (System Application and Products) was initiated by SAP AG originated in Germany. It is an enterprise resource planning software product that enables organizations in integrating various business processes through a single unified system. Since SAP started its journey concentrating on inventory management, it has come a long way adopting various modules for different processes in an organization. Today, SAP has been adopted by host of companies from across the globe to enhance the process works in various departments. From human resource management to sales and distribution and from financial accounting to controlling, SAP has a wide range of modules for different job areas.
Components of SAP SD Module
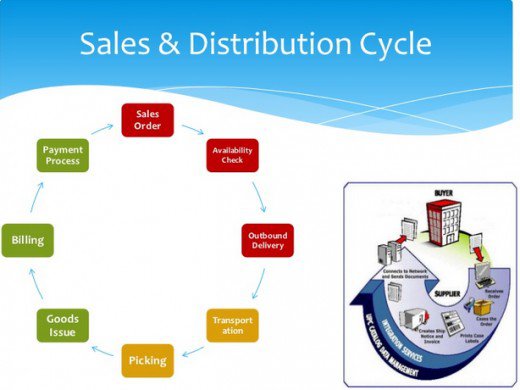
SAP-SD-MD (Master Data): SAP SD user includes master data and the process involves tracking of each and every transaction within the data. The sales and distribution master data includes of customer master data, material master data, pricing conditions record, output records and credit management. From order to cash process, entire flow is being recorded in this module.
SAP-SD-BF (Basic Functions): SAP SD configuration results in an effective process across all basic functions involved in sales and distribution area. Here, examples of basic functions can be pricing, output etc. The amount of pricing used for a particular sale and the output result from the same and so on.
SAP-SD-SLS (Sales): As the term suggests, SAP SD sales handles minute details of every sale that is taken place. From recording the product to customer details, pricing, feedback and the sales process, everything is tracked through this module.
SAP-SD-SHP (Shipping): Sales are closely related to shipping and delivery. A Product needs to be rightly shipped and delivered to the customer. There are different methods of shipping and this module track each one used for each delivery. The entire process from being shipped to delivered or return back is recorded through this module.
SAP-SD-TBA (Transportation): This SAP SD component works closely with the above shipping module. A product can be either couriered or manually delivered. The mode of transportation is different for each one and is being tracked through this module.
SAP-SD-FTT (Foreign Trade): This component helps a department to handle the data related to foreign trade including both imported products and products exported outside. This module works best for enterprises involved with trade across nations.
SAP-SD-BIL (Billing): Billing is a major part in sales. Customers can pay either online using debit or credit card, through cash on delivery, or by using pay pal account and so on. To maintain a proper track for future reference, each bill detail is recorded through this module.
SAP-SD-CAS (Sales Support): From selling a product to maintaining it for a process, customers constantly interact with the sales team. The data exchanged between the sales team and customers while delivering support for a product is recorded and reported through this module.
These are some of the multiple components involved in SAP SD user for effective process work within sales and distribution job area. There are various advantages of SAP SD configuration and few of these are mentioned as below.
Advantages of SAP SD Configuration in Enterprises:
Track of sales transactions
Record or pre-sale and post-sale process
Tracks sales data along with team performance
Defined process for sales and distribution
Categorization of diverse sales and process
Effective management of sales documents in a unified system